A blue screen error can be frustrating, especially when it prevents your computer from functioning properly. One of the most common errors that users encounter is “System Thread Exception Not Handled.” This error usually occurs due to driver-related issues, corrupt system files, or hardware conflicts.
If your Windows PC crashes with this message, you are not alone. This guide explains why this error happens and provides step-by-step fixes to get your system running again.
What Does “System Thread Exception Not Handled” Mean?
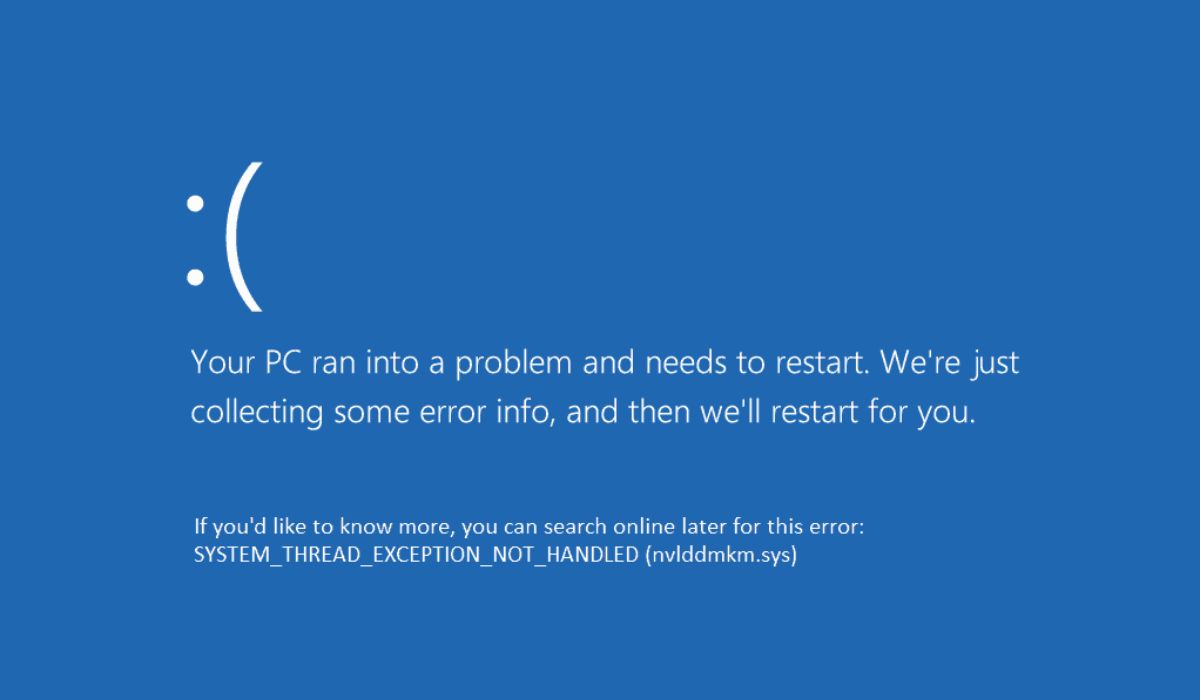
This error occurs when a system thread in the Windows operating system encounters an issue it cannot handle, forcing the computer to crash. It often appears with a specific driver file name, like nvlddmkm.sys, atikmpag.sys, or usbxhci.sys, which indicates the driveis r causing the problem.
The error usually appears:
- During Windows startup
- When updating device drivers
- After installing new hardware or software
- While running graphics-intensive applications
If left unresolved, it can cause your computer to enter a continuous restart loop, making normal usage impossible.
Common Causes of This Error
Several factors can trigger this BSOD. Identifying the root cause can help fix the issue faster.
- Outdated or Corrupt Drivers: Most cases of this error occur due to incompatible or damaged drivers. Graphics card drivers from NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel are the most common culprits. Network and chipset drivers can also cause system crashes.
- Faulty Windows System Files: Corrupted system files can prevent Windows from functioning properly and lead to crashes. This can happen due to unexpected shutdowns, failed updates, or malware infections.
- Overclocking and BIOS Issues: If you have overclocked your CPU or GPU, unstable clock speeds may cause the system to crash. An outdated or misconfigured BIOS can also trigger BSOD errors.
- Conflicts from Recent Software or Windows Updates: Some third-party applications or recent Windows updates can interfere with system processes, leading to driver failures.
- Hardware Problems: A failing GPU, faulty RAM, or SSD issues can also contribute to this error. Running diagnostic tests can help rule out hardware failure.
Step-by-step fixes for “System Thread Exception Not Handled”
Follow these solutions to resolve the issue and prevent further crashes.
Fix 1: Update, Roll Back, or Reinstall Drivers
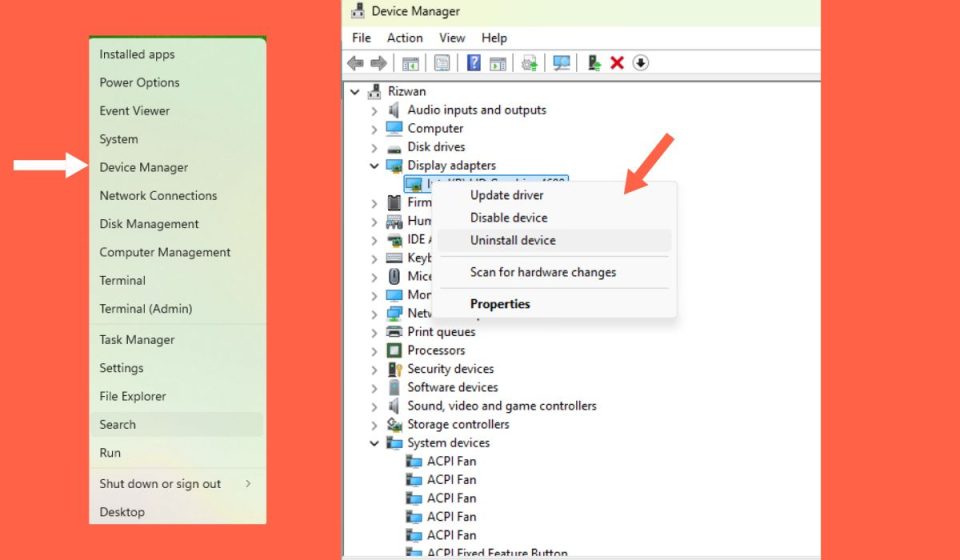
Since outdated drivers are the most common cause, updating or reinstalling them is a good starting point.
- Open Device Manager by pressing
Win + Xand selecting it from the list. - Expand the category related to the driver causing the error (e.g., Display adapters for GPU drivers).
- Right-click the affected driver and choose Update driver.
- Select Search automatically for drivers and let Windows find the latest version.
- If the issue started after an update, select Back Roll Driver instead.
For manual updates, visit the official website of your device manufacturer (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) and download the latest driver.
Fix 2: Boot into Safe Mode and Remove Problematic Drivers
If your computer keeps restarting, booting into Safe Mode can allow you to remove faulty drivers safely.
- Please turn off your PC and power it on. As soon as it starts, press F8 or Shift + F8 repeatedly until the Advanced Startup screen appears.
- Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings and click Restart.
- Choose Enable Safe Mode with Networking.
- Open Device Manager, right-click the problematic driver and select Uninstall device.
- Restart your PC and let Windows reinstall the default driver.
This method helps resolve issues caused by corrupted or incompatible drivers.
Fix 3: Run System File Checker and Windows Repair Tools
If damaged system files are causing the error, running repair tools can fix them.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (
Win + X> Command Prompt (Admin)). - Type:sfc /scannow
Press Enter. This scans for and repairs corrupted files.
- After completion, type:dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
This runs the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool to fix deeper system issues.
- Restart your PC and check if the problem persists.
Fix 4: Use System Restore or Reset Windows
If the error started after a recent change, rolling back to a previous system state might resolve it.
- Press
Win + R, typerstrui, and hit Enter to open System Restore. - Select a restore point before the error starts and follow the prompts.
If no restore points are available, consider resetting Windows:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Under Reset this PC, click Get Started and choose Keep My Files.
- Follow the instructions to reinstall Windows while keeping personal data.
This method helps if the issue is due to corrupt system settings or faulty updates.
Fix 5: Check for Hardware Issues
If none of the above solutions work, faulty hardware could be causing the error. Run these tests:
- Check RAM using Windows Memory Diagnostic
- Press
Win + R, typemdsched.exe, and hit Enter. - Choose Restart now and check for problems.
- Press
- Test GPU stability
- Use GPU-Z or MSI Afterburner to check for overheating.
- If using an NVIDIA or AMD card, try running with a different GPU driver version.
- Check SSD for errors
- Open Command Prompt (Admin).
- Run:chkdsk /f /r
- Restart your PC to allow the scan to complete.
When to Seek Professional Help

If none of the solutions work and your PC continues to crash, advanced troubleshooting may be necessary. At this stage, identifying the exact cause of the error requires deeper system analysis.
One way to diagnose the issue is by analyzing minidump files using WinDbg. Minidump files are automatically created when Windows encounters a critical error and contain valuable information about what caused the crash. Using Windows Debugging Tools, you can open these files and find details about the faulty driver or system component responsible for the BSOD.
Another helpful tool is Event Viewer, which logs all system activities, including errors and warnings. By searching for critical system errors around the time of the crash, you may find patterns that indicate which driver or hardware component is failing. Look for logs related to kernel failures, driver crashes, or unexpected shutdowns.
If you are unable to diagnose the issue on your own, contact Microsoft Support or your device manufacturer. Microsoft provides official troubleshooting support for Windows-related matters, and hardware manufacturers such as NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, and Dell offer technical support for device-specific driver problems. If the error is hardware-related, they may guide you on possible repairs or replacements.
Preventing Future BSOD Errors
To keep your system stable and avoid future errors:
- Regularly update drivers from official sources.
- Avoid installing unverified third-party software.
- Keep Windows updated but pause updates if issues arise.
- Monitor hardware health using diagnostic tools.
Taking these precautions can help maintain a smooth and reliable system.
Conclusion
The “System Thread Exception Not Handled” error is often linked to corrupt drivers, system file issues, or hardware malfunctions. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, most users can resolve the issue and restore their system’s stability.
Keeping device drivers updated, running system diagnostics, and maintaining hardware health are key steps to preventing future BSOD errors. If the issue persists despite these fixes, professional help from Microsoft Support or hardware manufacturers may be necessary.
If you found this guide helpful, share it with friends who might be facing the same issue. For more troubleshooting guides and tech solutions, visit our Blog section for expert advice on Windows errors and system fixes.
