CSM, or Compatibility Support Module, is a feature in BIOS that allows modern UEFI-based systems to support legacy booting methods. This means that if a system has older hardware or an operating system that does not support UEFI, enabling CSM can allow the system to boot properly. However, as more computers transition to UEFI-only environments, many users wonder whether CSM should be enabled or disabled for optimal performance and compatibility.
This guide will explain CSM, how it works when to enable or disable it, and how it affects system booting.
What Is CSM in BIOS?
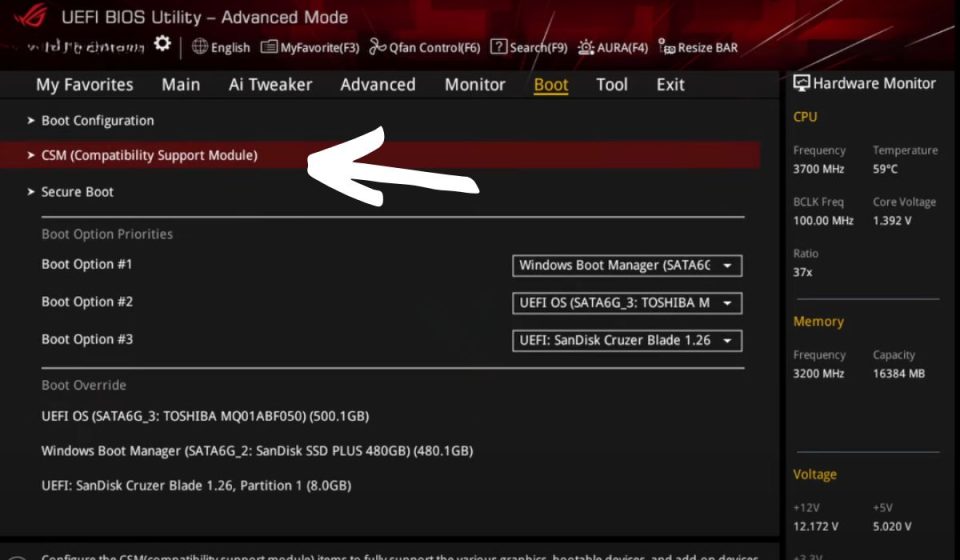
CSM, or Compatibility Support Module, is a part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) firmware that allows modern systems to boot using legacy BIOS-based methods. It enables computers to run older operating systems and work with devices requiring legacy BIOS boot mode instead of UEFI.
CSM is useful for users who:
- Are running older versions of Windows (Windows 7, XP, or Linux distributions that do not support UEFI).
- Older hard drives should be formatted with MBR (Master Boot Record) instead of GPT (GUID Partition Table).
- Need to boot from legacy devices, such as older network cards or expansion cards.
While CSM can help with backward compatibility, disabling it allows modern systems to take full advantage of UEFI features such as Secure Boot, faster boot times, and improved security.
CSM vs. UEFI: What’s the Difference?
UEFI and CSM serve different purposes when booting a computer. Understanding their differences helps determine when to enable or disable CSM.
| Feature | UEFI Mode | CSM (Legacy Mode) |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Speed | Faster boot times | Slower boot due to legacy compatibility |
| Partition Type | Uses GPT (GUID Partition Table) | Uses MBR (Master Boot Record) |
| Secure Boot | Supports Secure Boot for added protection | No support for Secure Boot |
| Compatibility | Works with modern OS and hardware | Supports older OS and hardware |
| Graphics Support | Supports high-resolution pre-boot interfaces | It uses a basic low-resolution BIOS interface |
Modern systems use UEFI as the default boot mode, and CSM is often disabled by default unless legacy support is needed.
Should You Enable or Disable CSM?
Enable or disabling CSM depends on your hardware and operating system requirements.
When to Enable CSM
- You are using Windows 7, XP, or older Linux versions that do not support UEFI.
- Your hard drive is formatted with MBR instead of GPT.
- You have older peripherals (e.g., PCI expansion cards, network adapters) that require legacy BIOS support.
- You are booting from an older external drive or USB device that only supports legacy BIOS mode.
When to Disable CSM
- You are running a modern OS like Windows 10 or Windows 11, which supports UEFI.
- Your storage device is formatted with GPT, which Secure Boot requires.
- You want faster boot times and improved security.
- You need to enable Secure Boot, which is incompatible with CSM.
- Your motherboard manufacturer recommends disabling CSM for stability and performance.
If your system is fully UEFI-compatible, disabling CSM for a more secure and efficient boot process is best.
How to Enable or Disable CSM in BIOS
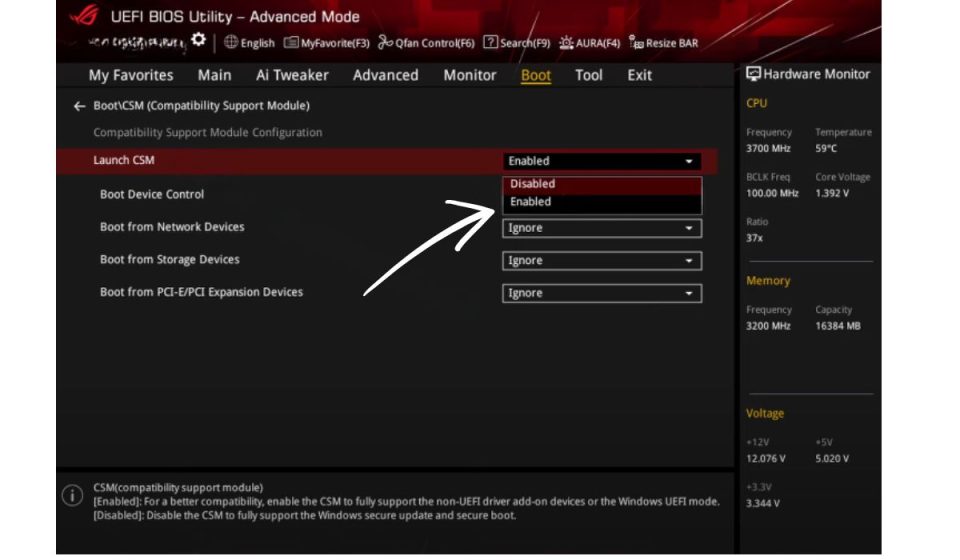
If you need to change the CSM setting, follow these steps:
- Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually F2, F12, Del, or Esc) to enter BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Navigate to the Boot or Advanced Settings tab.
- Locate the CSM (Compatibility Support Module) option.
- Choose Enable if you need legacy BIOS support or Disable to switch to full UEFI mode.
- If switching to UEFI mode, make sure your hard drive is formatted as GPT and Secure Boot is enabled.
- Save changes and exit the BIOS. Your system will reboot with the new settings.
Note: If you disable CSM and your system fails to boot, you may need to reinstall Windows using UEFI mode.
CSM and Boot Errors: Troubleshooting Issues
Disabling CSM can sometimes lead to boot issues if your system is not configured correctly for UEFI. Here’s how to fix common problems:
- “No bootable device found” error – This means your OS is installed in legacy mode, but UEFI is enabled. You may need to reinstall Windows using GPT partitioning.
- Windows doesn’t start after disabling CSM. Check if your storage drive is formatted with MBR instead of GPT. You can convert MBR to GPT using Windows Disk Management or Diskpart.
- Legacy USB devices are not detected. Some older USB drives and peripherals may require CSM to be enabled. If your device isn’t recognized, try booting with CSM on.
To avoid issues, ensure your operating system, storage drive, and BIOS settings are aligned with UEFI or legacy mode.
CSM and GPT/MBR Partition Compatibility
The partition style of your hard drive determines whether CSM should be enabled or disabled. If your drive uses MBR (Master Boot Record), it is compatible with CSM/Legacy BIOS and older operating systems. On the other hand, a GPT (GUID Partition Table) drive is designed to work with UEFI mode and supports Secure Boot for improved security and performance. If you plan to switch from CSM to UEFI, it is essential to check your drive’s partition style first to ensure compatibility.
To check your drive’s partition style:
- Open Disk Management by pressing Windows + X and selecting Disk Management.
- Right-click the disk you want to check and select Properties.
- Click on the Volumes tab and look for the Partition Style field, indicating whether it is MBR or GPT.
If your drive is MBR, you may need to convert it to GPT before disabling CSM to prevent boot errors.
Does CSM Affect Gaming Performance?

CSM does not directly impact gaming performance but can affect overall system efficiency and compatibility. While enabling CSM allows older hardware and legacy software to function, it may limit some of the advanced features of modern gaming systems.
Disabling CSM and switching to UEFI mode can improve boot speed, allowing your system to start up faster and load games faster. Since UEFI is optimized for modern technology, it provides better stability and support for newer hardware.
Many modern GPUs, including NVIDIA and AMD graphics cards, are designed to work best with UEFI firmware. Some newer models even require UEFI, meaning enabling CSM could lead to compatibility issues or reduced performance.
Disabling CSM is highly recommended for gamers using Windows 10 or Windows 11. It enables Secure Boot, which enhances system protection and ensures full compatibility with the latest hardware advancements, resulting in a smoother gaming experience.
Final Thoughts
CSM BIOS is a helpful feature for supporting older operating systems and hardware, but it is becoming less necessary as modern devices transition to full UEFI mode. If you are using newer hardware, an SSD with GPT, and Windows 10/11, it’s best to disable CSM for better security and performance.
However, if you rely on older hardware or software, enabling CSM may be necessary to ensure system compatibility. Before making changes, always back up your data and confirm your drive’s partition format to prevent boot issues.
Do you use CSM or UEFI mode on your system? Share your experience in the comments below!
